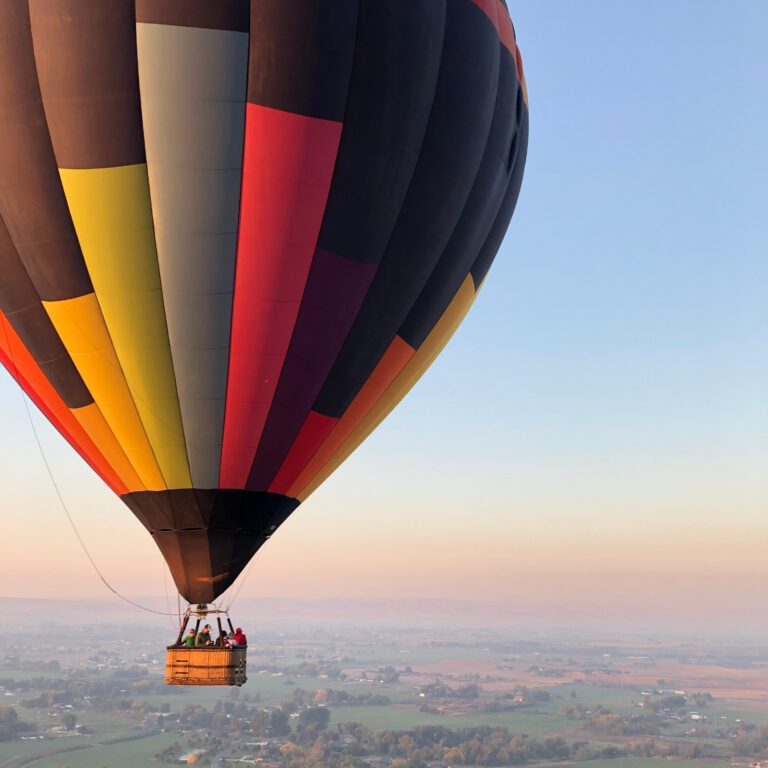
Introduction to Hot Air Balloons
Hot air balloons have fascinated people for centuries. They are a magical combination of science and adventure, allowing human flight in a visually stunning way. The beauty of a hot air balloon lies not just in its colorful design but also in the principles of physics that enable it to soar into the sky. Understanding how a hot air balloon works requires grasping a few key concepts, such as buoyancy, heat, and the properties of air.
The basic concept behind a hot air balloon is relatively simple. Hot air rises because it is less dense than the cooler air surrounding it. By heating the air inside a large balloon, the pilot can create a buoyant force that lifts the balloon off the ground. This article will explore the mechanics of hot air balloons, their components, safety considerations, and their history. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how hot air balloons operate.
The Physics of Hot Air Balloons
The Principle of Buoyancy
The operation of a hot air balloon is primarily based on the principle of buoyancy, which is defined by Archimedes’ principle. This principle states that an object immersed in a fluid experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces. In the case of a hot air balloon, the fluid is the surrounding air.
When the air inside the balloon is heated, it expands and becomes less dense than the cooler air outside. As a result, the hot air balloon rises. The cooler, denser air outside exerts more pressure on the balloon than the hot air inside, creating lift. This principle is central to flight, whether in hot air balloons or airplanes, as they all depend on differences in air density to achieve altitude.
Heating the Air
To produce hot air, a burner system is used in hot air balloons. This burner typically uses propane as fuel. When the propane ignites, it creates a flame that heats the air inside the envelope of the balloon. The burner is usually mounted above the basket, directly below the envelope.
Effective heating is crucial for achieving lift. The burner must provide enough heat to raise the temperature of the enclosed air significantly. As the air inside the balloon reaches higher temperatures, the volume of the air expands while its density decreases. The pilot can control the amount of heat produced by regulating the propane flow, allowing for precise altitude adjustments.

Components of a Hot Air Balloon
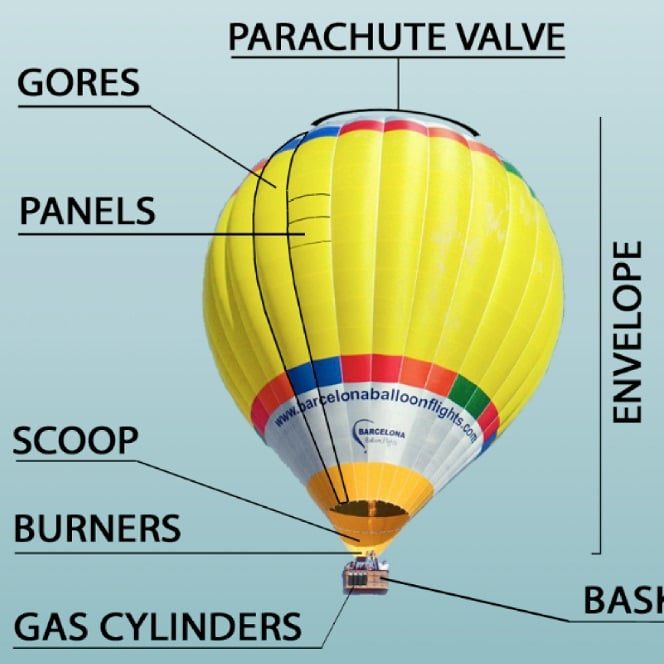
The Envelope
The envelope is the large, balloon-like structure that holds the hot air. Typically made from lightweight, heat-resistant fabric such as nylon or polyester, the envelope is designed to withstand the stresses of flight. It is constructed consisting of the top section, known as the crown, and the side panels.
The shape of the envelope is carefully created to maximize lift while maintaining stability in flight. There are several designs available, but they are generally tear-shaped to enhance aerodynamics. Additionally, the fabric is often coated with a heat-resistant layer to prevent damage from the burner’s heat.
The Basket
The basket, also referred to as the gondola, is the part of the hot air balloon that carries the pilot and any passengers. Typically made from wicker or a lightweight composite material, the basket provides a safe and sturdy structure.
Inside the basket, there are usually safety harnesses to secure passengers during flight. The basket also houses fuel tanks for the burner, and many designs feature a protective skirt around the edges to keep passengers safe. Additionally, the basket is designed to be as lightweight as possible while providing strength and durability for various flight conditions.
Operating a Hot Air Balloon
Preparing for Flight
Before takeoff, the pilot must complete several preparations. First, they check the weather conditions to ensure safe flying. Wind, temperature, and visibility are critical factors that can affect flight. Safe operating conditions are essential for a successful and safe flight.
Next, the pilot assembles the balloon by laying out the envelope and attaching it to the basket. The burner is positioned and connected to the fuel tanks. Once everything is in place, the balloon is inflated with cold air using a portable fan. This initial inflation is crucial before heating the air inside the balloon.
Takeoff and Flight Control
To initiate the flight, the pilot ignites the burner, heating the air inside the envelope. As the air warms, the balloon will begin to rise. The pilot can assess the altitude by observing the landscape below and adjusting the burner as necessary.
Controlling the hot air balloon is primarily achieved through heat management. By increasing the burner’s flame, the pilot can ascend. Conversely, allowing the air to cool or venting hot air through a parachute valve at the top of the envelope will lower the balloon. This system enables the pilot to navigate the skies with relative ease.
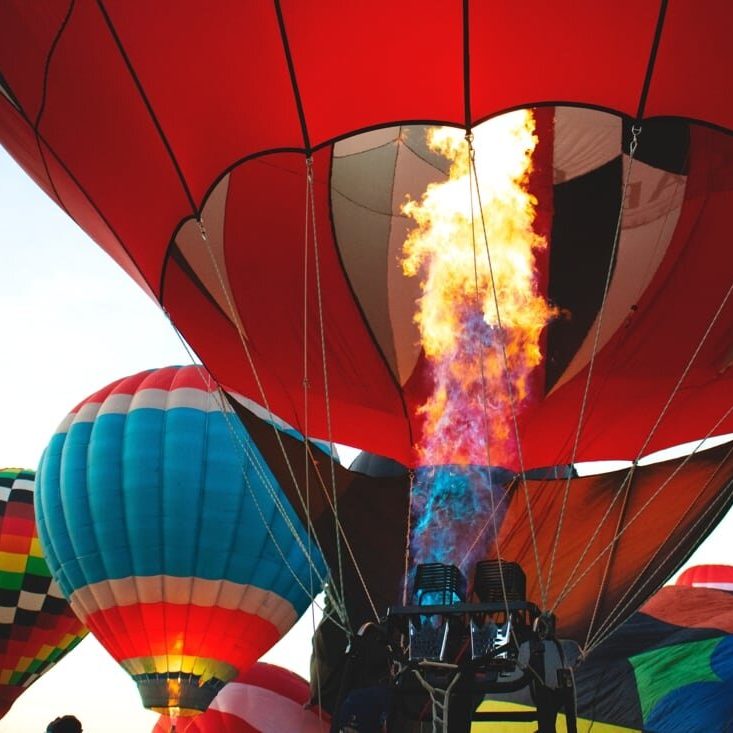

Safety Considerations
Pre-Flight Safety Checks
Safety is paramount when operating a hot air balloon. Before each flight, thorough checks must be conducted to ensure everything is in working order. The pilot should inspect the envelope for leaks, the burner for proper operation, and the basket for structural integrity.
Additionally, pilots should evaluate weather conditions and confirm that they are appropriate for flight. Understanding wind patterns and potential turbulence is crucial for ensuring a safe journey. Pre-flight planning includes route assessment and contingency measures for various scenarios, such as changing weather or emergency landings.
In-Flight Safety Protocols
While in-flight, safety protocols must be followed diligently. Pilots should maintain clear communication with their crew on the ground, who can provide support during landing. Regular monitoring of fuel levels and temperature inside the envelope is vital for maintaining safe operations.
Passengers should also be informed about safety procedures. This includes the importance of remaining seated and secured during takeoff and landing. Understanding how to safely exit the basket in case of an emergency is essential. Educational briefings can ensure that everyone onboard feels secure and confident throughout the flight.
The Evolution of Hot Air Balloons
Historical Significance
Hot air balloons date back to the 18th century, when the Montgolfier brothers flew the first passengers in 1783. This initial ascent marked the beginning of human flight. Since then, many advancements have been made in balloon design, materials, and technology.
The history of hot air balloons is filled with exciting stories of exploration and adventure. Early balloonists experimented with different fuels, envelope shapes, and flight techniques. The advent of synthetic fabrics in the 20th century revolutionized hot air balloon construction, making them more durable and efficient.
Modern Developments
Today, hot air balloons continue to capture public imagination. They are frequently featured in festivals, adventure tourism, and even scientific research. New technologies have improved fuel efficiency and safety features, making hot air ballooning more accessible than ever.
Hot air balloon festivals draw crowds, offering opportunities for rides alongside stunning views and communal experiences. Enthusiasts engage in competitive events, highlighting skill, creativity, and camaraderie among balloonists. The combination of art and science behind hot air balloons makes them appealing to a diverse range of individuals, from thrill-seekers to families looking for memorable experiences.
Conclusions: The Magic of Hot Air Balloons
In conclusion, hot air balloons represent a remarkable fusion of science and adventure. Their unique operation relies on the principles of buoyancy, heat, and aerodynamics, making them a fascinating subject of study. From their rich history to the intricacies of modern flight, hot air balloons continue to inspire wonder.
Understanding the components, operation, and safety features of hot air balloons ensures that both pilots and passengers can enjoy a thrilling experience. As technology advances, hot air ballooning becomes more accessible, allowing more people to experience the joy of flight.
Hot air balloons invite us to explore the skies and appreciate the beauty of our surroundings from a new perspective. Whether you are an aspiring balloonist or a curious traveler, the magic of hot air balloons will always have a special place in the world of aviation.
