Synchronized swimming has long been a captivating event in the synchronized swimming Olympics, blending athleticism, artistry, and teamwork in a mesmerizing display. As one of the most graceful and demanding sports, synchronized swimming draws audiences with its intricate routines and exceptional performers. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the history, techniques, key moments, and future of synchronized swimming in the Olympics, providing a deep understanding of this elegant sport.
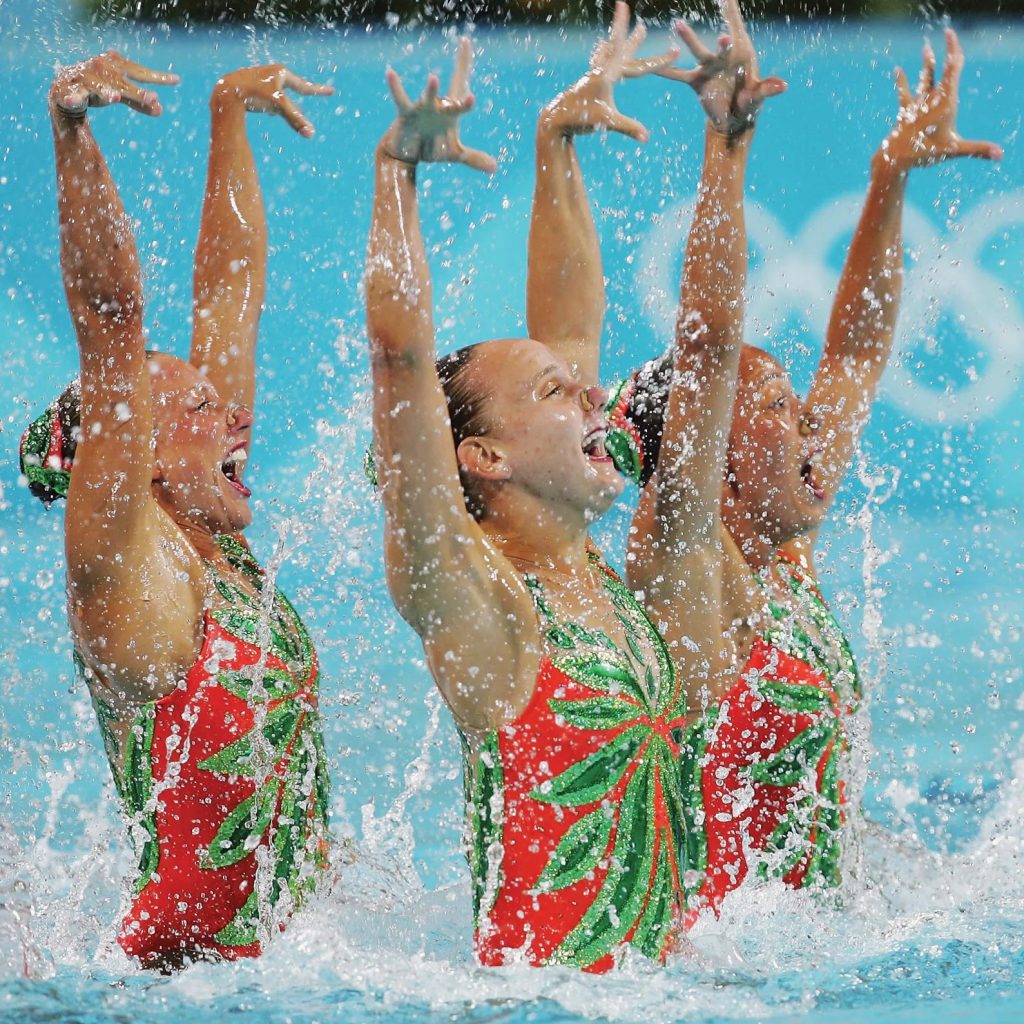 Overview of Synchronized Swimming at the Olympics
Overview of Synchronized Swimming at the Olympics
History and Introduction
Synchronized swimming first appeared in the Olympics as a demonstration sport in 1952. It became an official Olympic sport in 1984 during the Los Angeles Games. Initially, only duet events were held at the Olympics. The sport is performed in a swimming pool, combining dance, gymnastics, and swimming. Over the years, synchronized swimming has grown to feature dazzling routines and exceptional athleticism. Today, elite athletes showcase their skills, precision, and creativity on the Olympic stage.
Evolution of Synchronized Swimming Rules at the Olympics
The rules governing synchronized swimming have evolved significantly to ensure fairness and creativity. In the early years, scoring emphasized artistic impression over technical execution. Changes were introduced to balance artistry with technical performance. Technical routines now showcase precise skills, while free routines highlight artistic creativity. Costume guidelines and music selection rules ensure thematic consistency and cultural sensitivity. All scoring is conducted by specialized judges trained in both technical and artistic aspects. These refinements aim to enhance the integrity and global appeal of synchronized swimming.
Olympic Events and Categories in Synchronized Swimming
Synchronized swimming at the Olympics features two main events: duet and team competitions. These events highlight athletes’ precision, endurance, and seamless coordination. Each category tests different dynamics, making them equally exhilarating.
Duet and Team Competitions
Duet competitions involve two swimmers performing synchronized routines. The routines are meticulously crafted and synced to music. The pair must exhibit flawless timing and chemistry to impress judges. They also perform technical elements, such as lifts and spins, to showcase their versatility.
Team competitions include eight swimmers performing complex routines together. Team routines are grander, with intricate formations and patterns. They often include daring and dynamic lifts to captivate the audience. Perfect synchronization among all eight team members is critical for a high score.
Both events allow athletes to express their creativity through choreography. They blend athletic skills with artistic elegance, representing the essence of synchronized swimming at the Olympics.
Scoring System and Judging Criteria
The scoring system in synchronized swimming combines artistic and technical judging. Judges evaluate technical elements, including precision of movements, height, and synchronization. Athletes’ mastery of required figures and transitions is critical here.
Artistic impression encompasses the theme, creativity, and overall choreography of the routine. Judges assess how well the routine matches the music and captivates the audience. Costumes and presentation also add to the overall artistic score.
Scores from both technical and artistic judges are combined for the final tally. This balanced scoring system ensures routines are judged holistically, blending athleticism and creativity.
Rules and Regulations in Olympic Synchronized Swimming
Synchronized swimming in the Olympics adheres to strict regulations to ensure a fair and competitive environment. These rules focus on team makeup, costumes, music, and overall performance integrity.
Eligibility and Team Composition Requirements
Olympic synchronized swimming teams abide by eligibility rules set by the International Swimming Federation (FINA). Athletes must meet age, nationality, and qualification standards to participate. Each country can enter teams for duet and team events, with athletes chosen through rigorous selection.
For team competitions, eight swimmers perform together, showcasing unity and synchronization. Duet events feature two athletes building chemistry and coordination to execute synchronized routines. Substitutions are allowed but must adhere to strict procedural guidelines.
Guidelines for Costumes and Music
Costumes in synchronized swimming must align with competition rules to maintain professionalism and sportsmanship. Outfits must be appropriate and ensure freedom of movement. They should avoid excessive embellishments to prevent distractions and safety issues.
Music plays a critical role in routines, driving the choreography and artistic performance. Guidelines require music choices to be culturally sensitive and free of offensive content. Synchronization between movements and music is essential for high artistic scores, highlighting creativity and emotional impact.
These strict rules safeguard the sport’s integrity, providing athletes a consistent and fair competitive platform.
How Synchronized Swimming is Scored at the Olympics
Synchronized swimming scoring focuses on both technical precision and artistic performance. Judges consider several aspects, including synchronization, creativity, and execution. The system ensures fairness by evaluating all elements of the routine.
Technical Routines vs Free Routines
Synchronized swimming includes technical and free routines. Each serves a specific purpose in the scoring process.
Technical routines require athletes to perform specific moves in a set sequence. This ensures consistency and highlights skill. Judges assess precision, synchronization, and mastery of required elements. Mistakes or lack of clarity result in point deductions.
Free routines allow athletes to showcase artistic creativity and unique choreography. There are no fixed elements, enabling flexibility and expression. Judges score based on innovation, music interpretation, and overall impact. This fosters individuality while emphasizing performance quality.
Balancing the two routine types ensures a fair mix of skill and artistry in competition.
Point Allocation for Performance and Artistic Impression
Judges evaluate performances using a detailed point system. Scores are divided into technical and artistic categories.
- Technical Performance: Judges assess precision, synchronization, execution, and difficulty of movements. Athletes must meet high standards to earn top scores.
- Artistic Impression: This includes choreography, theme, and connection with music. Judges value creativity and emotional delivery. Costumes and audience engagement also factor into the score.
Both sets of scores combine into a final total. This balanced system rewards athletes who excel in athleticism and creativity. It ensures that every performance aspect contributes to the final ranking.
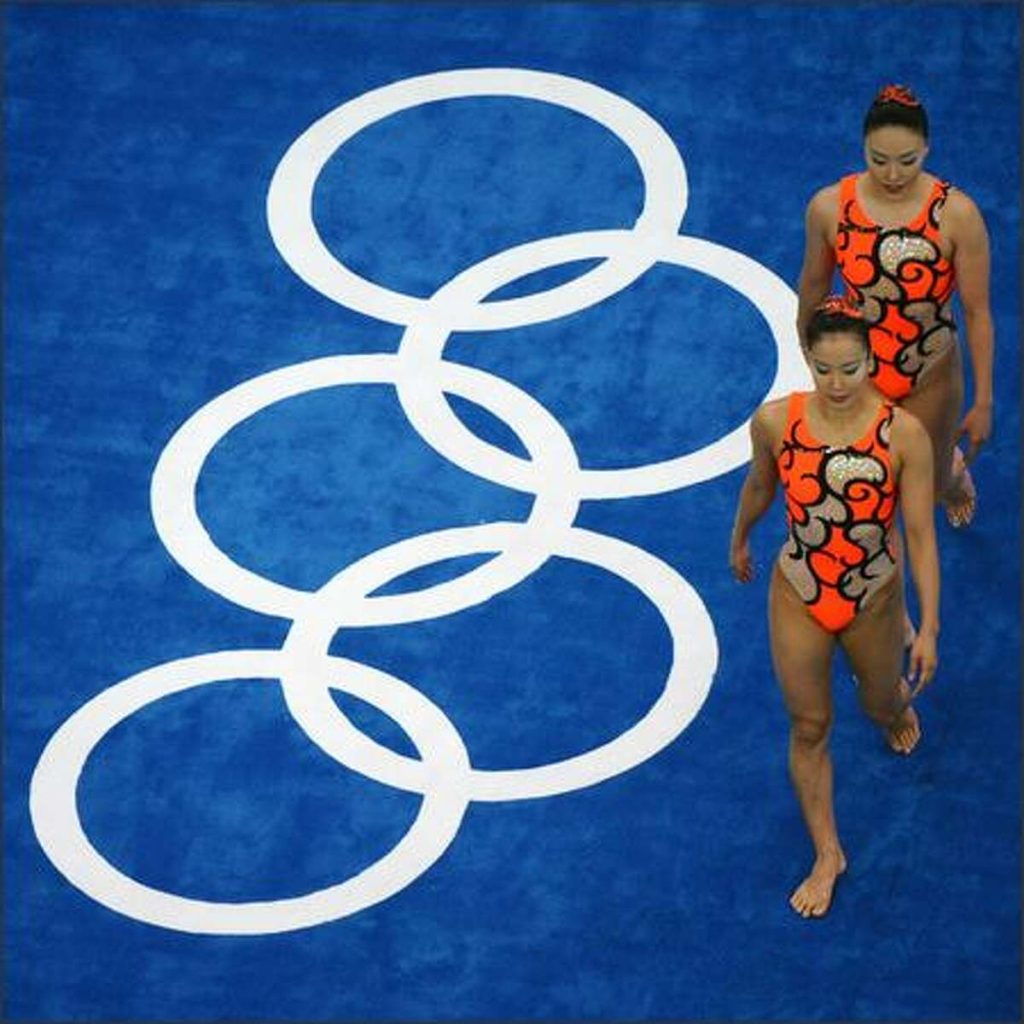 Training and Preparation for Olympic Athletes
Training and Preparation for Olympic Athletes
Preparing for synchronized swimming at the Olympic level requires intense training and focus. Athletes dedicate years to perfecting both their physical skills and mental endurance. Success demands discipline, teamwork, and creativity.
Physical and Mental Preparation
Synchronized swimming requires athletes to maintain peak physical condition. Swimmers spend hours building strength, flexibility, and endurance. Core strength is vital for maintaining body control during lifts and spins. Endurance is just as crucial since routines can last several minutes without touching the pool floor.
Swimmers follow rigorous cardiovascular and strength training regimens. Exercises like swimming laps, pilates, and weightlifting are common. Flexibility is another focus, achieved through stretching and specialized training.
Mental preparation is equally essential. Athletes practice visualization techniques to mentally rehearse routines. It helps them anticipate movements and stay focused under pressure. Breath control exercises also prepare them for extended underwater sequences. Meditation and mindfulness training help reduce stress and maintain composure during competitions.
Strategies for Synchronization and Choreography
Perfect synchronization is crucial in this sport. Athletes train in perfect sync with teammates, practicing routines repeatedly until movements become automatic. Timing drills and listening to music cues help refine their performance.
Choreography is a collaborative effort involving the athletes and coaches. They design routines that highlight creativity and athletic skill. Teams focus on integrating challenging lifts, spins, and patterns into their performances. Movements must align seamlessly with the music to create an emotional connection.
Underwater coordination is another key aspect of training. Swimmers spend time perfecting movements below the surface, ensuring flawless execution even when submerged. This includes practicing holding their breath for long periods while performing complex routines.
By combining physical and mental preparation with advanced choreography techniques, synchronized swimmers achieve Olympic-level mastery. These efforts showcase the beauty and athleticism of the sport on the global stage.
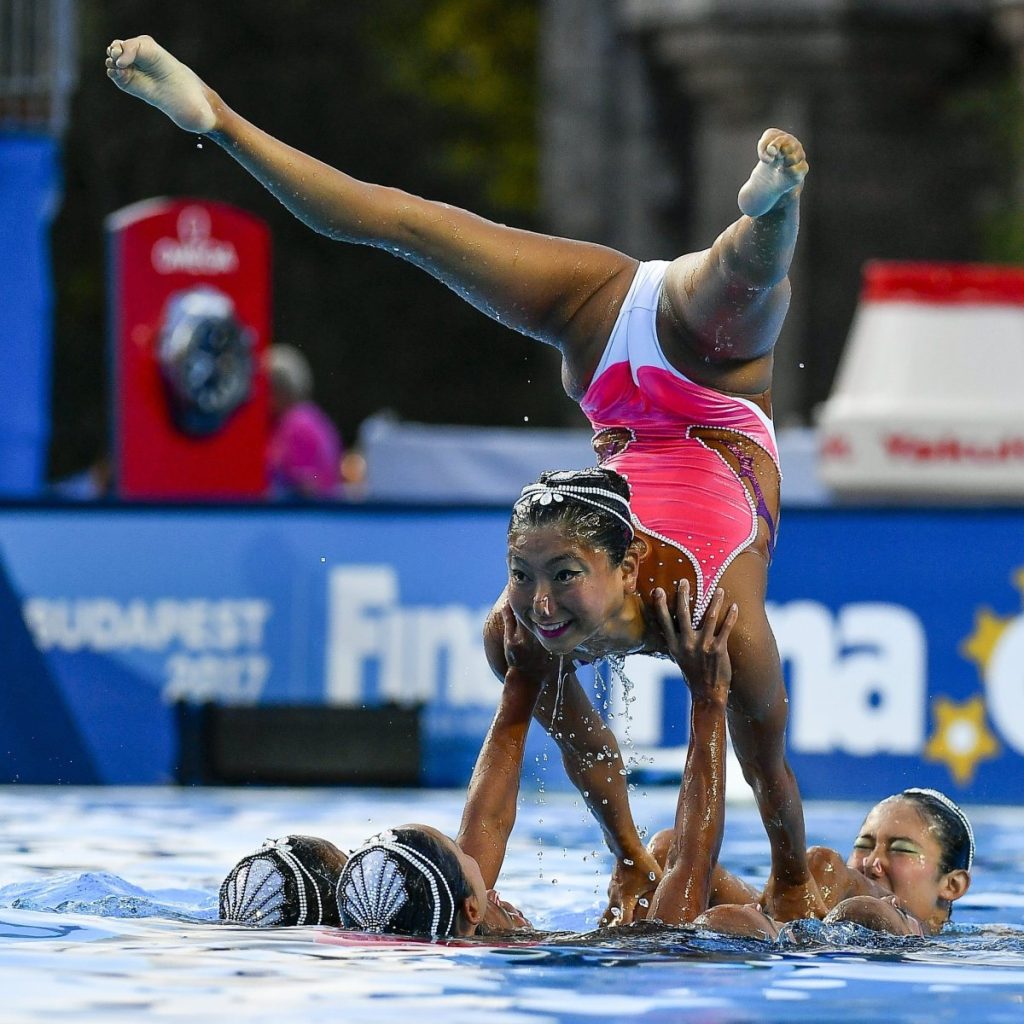 Iconic Moments and Highlights in Olympic Synchronized Swimming
Iconic Moments and Highlights in Olympic Synchronized Swimming
Memorable Performances in Olympic History
Synchronized swimming has delivered breathtaking moments across Olympic history. These performances reflect artistry and skill.
One such moment came during the 1996 Atlanta Olympics. The U.S. team performed an iconic routine called “The Piece.” Their dramatic choreography and perfect synchronization earned them the gold medal and international acclaim. This routine became a benchmark for team competitions.
Another standout occurred in the 2008 Beijing Olympics. Russia’s duet team, Natalia Ishchenko and Anastasia Davydova, amazed audiences with their “Mermaids” routine. Their incredible lifts and underwater precision secured them a gold medal. Their performance showcased unmatched artistic creativity and technical mastery.
At the 2016 Rio Olympics, China’s team made headlines with their “Legend of the Phoenix” routine. The performance combined intricate formations and cultural storytelling. It was a stunning display of artistic excellence that earned them a silver medal.
These memorable moments demonstrate how synchronized swimming blends athletic talent and creative expression. Each routine not only pushed boundaries but also elevated the sport’s prestige on the Olympic stage.
Celebrating Athletes Who Shaped the Sport
Many synchronized swimmers have redefined the sport through their groundbreaking achievements.
Natalia Ishchenko and Svetlana Romashina from Russia are iconic champions. Together, they won multiple Olympic gold medals, dominating duet and team events. Their precision and innovative routines inspired generations of athletes.
Gemma Mengual from Spain left a lasting legacy in the sport. She introduced fresh artistic elements that elevated synchronized swimming’s appeal. Her influence extended beyond her Olympic performances.
Another legend is Yuko Fujiki of Japan, known for her elegance and technical expertise. She consistently excelled under pressure, setting new standards for execution and synchronization.
These athletes not only won medals but also shaped synchronized swimming’s artistry and competitiveness. They contributed to the global recognition of the sport. Today, their legacies inspire young swimmers worldwide to excel in synchronized swimming at the Olympics.
Future of Synchronized Swimming in the Olympics
The future of synchronized swimming in the Olympics looks promising. The sport continues to adapt and evolve. Innovations and increased global interest are shaping its next chapter.
Innovations and Changes in Format
Synchronized swimming is embracing new technologies and ideas. Enhanced underwater cameras improve judging accuracy and showcase techniques. These cameras allow viewers to appreciate underwater movements better.
There is also discussion about adding mixed-gender events. Mixed-gender teams could bring diverse talent and expand creative choreography options. This change aims to attract wider audiences to the sport.
Rule modifications may occur to further balance technical and artistic aspects. For example, scoring systems might evolve to reward innovation more. Changes like this ensure synchronized swimming remains exciting and competitive.
Innovation isn’t limited to scoring or formats. Advanced training techniques, such as virtual routine simulations, are helping athletes achieve perfection. These tools prepare teams for high-pressure Olympic competitions.
Expanding Global Participation and Interest
Synchronized swimming is becoming popular worldwide. Efforts to engage more countries in the Olympics are growing. The International Swimming Federation (FINA) is promoting the sport through global events and workshops.
Countries with emerging talent have begun to challenge traditional powerhouses. This increases competitiveness, broadening synchronized swimming’s global appeal.
Grassroots programs are boosting participation in regions where the sport is less developed. These initiatives provide access to training resources and expert guidance.
More efforts are focusing on captivating younger audiences. Creative choreography, paired with social media campaigns, highlights synchronized swimming’s artistic charm. This bridges the gap between tradition and modernity.
Expanding global participation strengthens inclusion and talent diversity in Olympic synchronized swimming. It keeps the sport relevant and inspiring for athletes and fans worldwide.
 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is synchronized swimming in the Olympics?
Synchronized swimming, now known as artistic swimming, is an Olympic sport where athletes perform synchronized routines of elaborate moves in the water, accompanied by music. The sport combines elements of swimming, dance, and gymnastics, judged on technical execution and artistic impression.
How many synchronized swimming events are there in the Olympics?
As of the latest Olympics, there are two main events in synchronized swimming: the duet and the team competition. The duet involves two swimmers performing a routine together, while the team event features a group of eight swimmers executing a synchronized routine.
What are the main criteria for judging synchronized swimming in the Olympics?
Judging in synchronized swimming Olympics is based on technical execution, artistic impression, and synchronization. Judges assess the difficulty and precision of movements, the creativity and choreography of the routine, and how well the swimmers perform in harmony with each other and the music.
How do athletes qualify for synchronized swimming in the Olympics?
Athletes qualify for the Olympic synchronized swimming competition through their performance in international competitions such as the World Aquatics Championships and continental championships. National governing bodies select the top performers based on their rankings and results in these events.
Can men compete in synchronized swimming at the Olympics?
Currently, synchronized swimming at the Olympics is a female-dominated sport. However, there are ongoing discussions and initiatives to include male athletes in future Olympic synchronized swimming competitions, promoting gender inclusivity and diversity within the sport.
What training regimen do synchronized swimmers follow for the Olympics?
Olympic synchronized swimmers follow an intense training regimen that includes swimming laps, strength training, flexibility exercises, and routine practice. They also engage in mental training and team-building activities to enhance focus, coordination, and teamwork essential for high-level performances.
How has synchronized swimming evolved in the Olympics over the years?
Since its debut in 1984, synchronized swimming has evolved significantly in the Olympics. The addition of team events, the rebranding to artistic swimming, and the incorporation of more complex and creative routines have all contributed to the sport’s growth and increased competitiveness on the Olympic stage.
What are some memorable Olympic synchronized swimming performances?
Several performances have stood out in Olympic synchronized swimming history. The Russian team’s dominating routines, the United States’ groundbreaking performances in the early years, and innovative routines that blend storytelling with technical prowess are some of the most memorable moments in the sport’s Olympic journey.
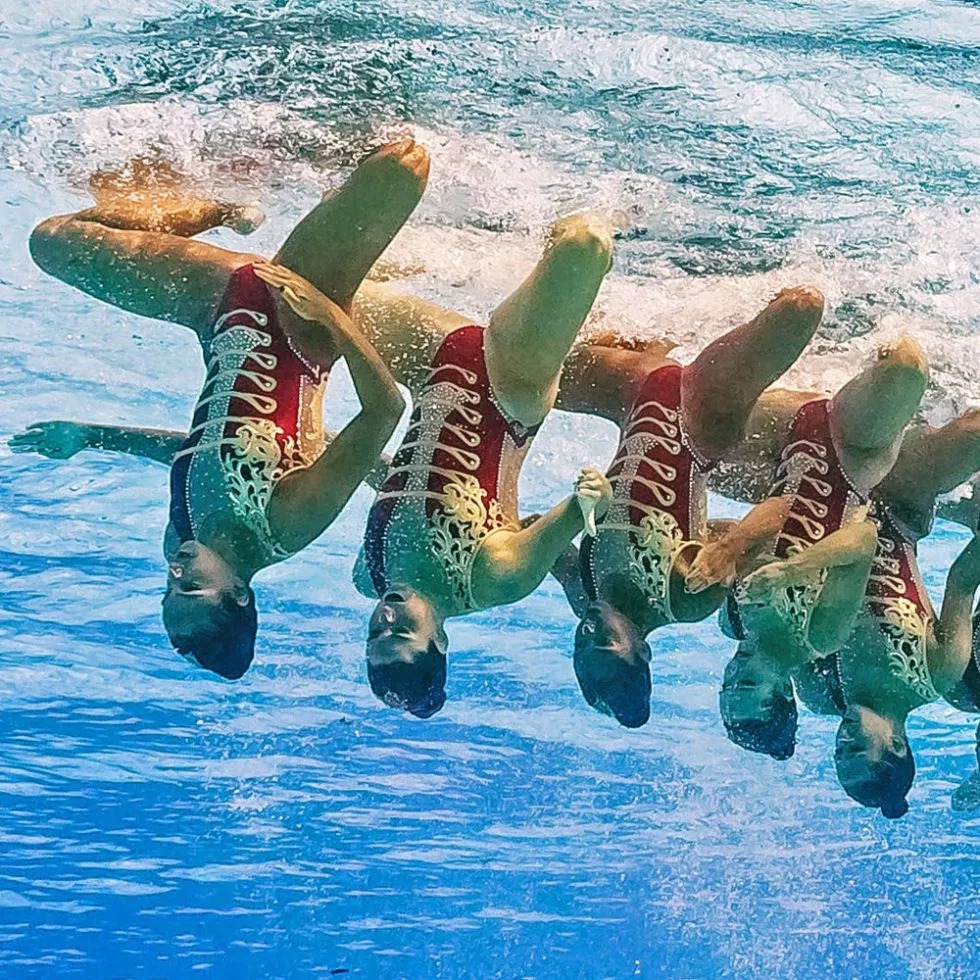 Conclusion
Conclusion
The synchronized swimming Olympics epitomizes the perfect harmony of athleticism and artistry, showcasing the dedication and skill of its athletes on a global stage. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a celebrated Olympic event, synchronized swimming continues to enchant audiences with its graceful and synchronized performances. As the sport evolves, embracing new trends and promoting inclusivity, the future of synchronized swimming in the Olympics looks brighter than ever. Whether you are a longtime fan or new to the sport, the synchronized swimming Olympics offers a unique and inspiring spectacle that highlights the extraordinary capabilities of its athletes. Dive into the world of synchronized swimming and witness the elegance and precision that make it a standout event in the Olympic Games.